One of the biggest and brightest stars in the night sky will momentarily disappear when an asteroid passes in front of it to produce a unique eclipse.
The rare and fleeting spectacle, which will run from Monday afternoon to early Tuesday, should be visible to millions of people along a narrow trail that stretches from Tajikistan and Armenia in central Asia, through Turkey, Greece , Italy and Spain, to Miami and the Florida Keys and, finally, to parts of Mexico.
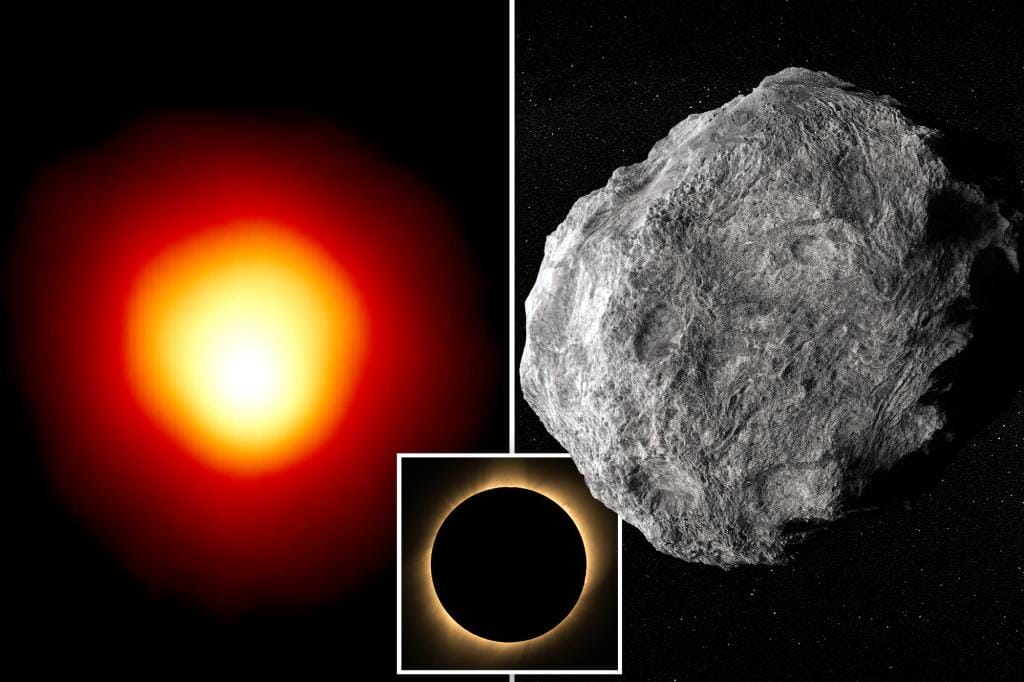
The star is Betelgeuse, a red supergiant in the constellation Orion.
The asteroid is Leona, an oblong space rock slowly rotating in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
Astronomers hope to learn more about Betelgeuse and Leona through the eclipse, which is expected to last no longer than 15 seconds.
Binoculars and small telescopes will improve the view for those who wish to catch a glimpse of this rare occasion. Christoph – stock.adobe.com
Observing an eclipse of a much fainter star near Leona in September, a Spanish-led team recently estimated that the asteroid was about 34 miles wide and 50 miles long.
Uncertainties remain about those predictions, as well as about the size of the star and its expansive atmosphere. It is unclear whether the asteroid will obscure the entire star, producing a total eclipse.
Rather, the result could be a “ring of fire” eclipse with a tiny glowing rim around the star.
Scientists expect Betelgeuse to go supernova in a violent explosion within 100,000 years. Aliaksandr Marko – stock.adobe.com
If it is a total eclipse, astronomers are not sure how many seconds the star will completely disappear, perhaps up to 10 seconds.
“The scenario we will see is uncertain, which makes the event even more intriguing,” said astronomer Gianluca Masa, founder of the Virtual Telescope Project, which will offer a live webcast from Italy.
At an estimated distance of 700 light years, Betelgeuse is visible to the naked eye.
Binoculars and small telescopes will improve vision. One light year is equivalent to 5.8 trillion miles.
Betelgeuse is thousands of times brighter than our sun and about 700 times larger.
At only 10 million years old, Betelgeuse is considerably younger than the 4.6 billion-year-old Sun. Mopic – stock.adobe.com Betelgeuse is thousands of times brighter than our sun and about 700 times larger. AP
It is so large that if it replaced our sun, it would extend beyond Jupiter, according to NASA.
At only 10 million years old, Betelgeuse is considerably younger than the 4.6 billion-year-old Sun.
Scientists expect Betelgeuse to be short-lived, given its mass and the rate at which it burns through its material.
After countless centuries of varying brightness, Betelgeuse dimmed dramatically in 2019 when a huge amount of surface material was ejected into space.
The resulting dust cloud temporarily blocked starlight, NASA said, and within half a year, Betelgeuse was as bright as before.
Scientists expect Betelgeuse to go supernova in a violent explosion within 100,000 years.
Categories: Trending
Source: vtt.edu.vn