How does a solar storm affect our world and what is it made of? Does this cosmic event represent a danger to Earth? Here we examine the science behind this event, its impact on our planet and more.
Jump to
- What is a solar storm?
- When did the most recent solar storm occur?
- How did it affect our planet?
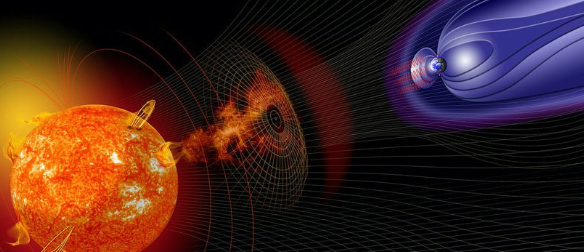
What is a solar storm?
Credit: Rainbow Symphony
A solar storm is a surface disturbance that sends charged particles and enormous amounts of energy into space. Upon arrival, these particles interact with the Earth’s magnetic field, causing geomagnetic disturbances. An event like this can affect satellites, power grids, and communication networks.
When did the most recent solar storm occur?

Credit: iStock
In early 2023, many warnings were issued about an impending solar storm that finally reached Earth on December 27.
This solar storm arrived after a celestial event that occurred on December 24. A magnetic filament eruption on the side of the Sun facing our planet triggered a coronal mass ejection (CME).
How did it affect our planet?
Spaceweather.com notes that only mild G1-class geomagnetic storms are possible on December 27; The accuracy of this prediction is still questionable. The uncertainty arises from the possibility that these storms barely graze or completely avoid the Earth’s magnetic field.
The Weather Channel speculates that northern Earth could be affected, although it would be a mild experience rather than a powerful geomagnetic storm.
During an 11-year cycle, a G1 class storm (the mildest on the scale, with a G5 storm being the strongest) occurs approximately every 900 days.
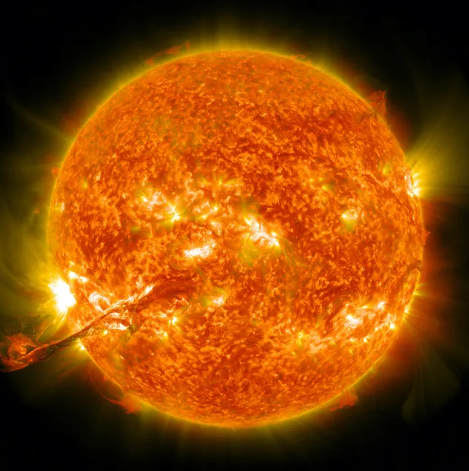

Credit: NASA
High-latitude areas can see dancing auroras, modest satellites and power grid disruptions, and increased radiation exposure for astronauts and aircraft crews.
Additionally, radio amateurs, pilots, sailors, and drone operators may experience communications disruptions.
what do you think about it? Let us know in the comments.
For more trending stories, follow us on Telegram.
Categories: Trending
Source: vtt.edu.vn
