Robotic surgery also known as robotic-assisted surgery is perhaps the most cutting-edge medical technology available today.
Today’s most extensively utilized method combines a camera with using tiny surgical instruments coupled to robotic arms. Surgeons use a monitor in the operating room to operating the robotic arms, which are often positioned in the same area as the operating table.
However, the viewing screen might be placed in a distant location, enabling doctors to conduct the surgery from afar.
The screen is part of a console, which enables surgical operations to be conducted while the surgeon sits in a sitting posture and displays a magnified three-dimensional image of the patient’s operative site.
Contrary to popular belief, robots do not conduct robotic surgery. Instead, the surgeon maintains total control of the robotic arms at all times. The robot acts as a tool and may be thought of as a type of helper to the surgeon, thus the phrase robotic-assisted surgery
Different Robotic Surgery Systems:
1. Da Vinci By Intuitive Surgical:
The Da Vinci Surgical System enables surgeons to execute a wide range of minimally invasive operations with clinically proven precision and accuracy.
The device may use for many procedures, including minimally invasive cardiac, colorectal, gynecological, head & neck, thoracic, urology, and general surgery.
The Surgeon Console, which controls the Patient Cart’s robotic gadgets, including several surgical tools and a camera, is used by the surgeon.
Over 1,700 da Vinci Systems are presently deployed in hospitals throughout the world, and this robotic surgical system has performed surgeries on over 775,000 patients.
With da Vinci devices used in about 75% of all prostate cancer procedures in the United States, this robotic platform has proven itself as a successful and dependable instrument.
2. Ion By Intuitive Surgical:
In February 2019, the FDA granted 510(k) approval to Intuitive’s Ion robotic surgical system. Using this robotic endoluminal device, surgeons may do noninvasive biopsies of the lung’s deepest regions.
The physician uses the robotic catheter to travel through the narrow and convoluted airways of the lung to reach regions of interest. Forceps and needles, for example, fit within the catheter and utilize it as a guide to reach the desired lung region.
Ion employs fiber optic shape-sensing technology to provide robotic control of the catheter’s location during navigation.
When the catheter reaches the correct location, it locks in place, giving the exceptional stability required for biopsy accuracy. Ion’s catheter rotates 180 degrees in all directions, allowing for fine-tuning in biopsy accuracy.
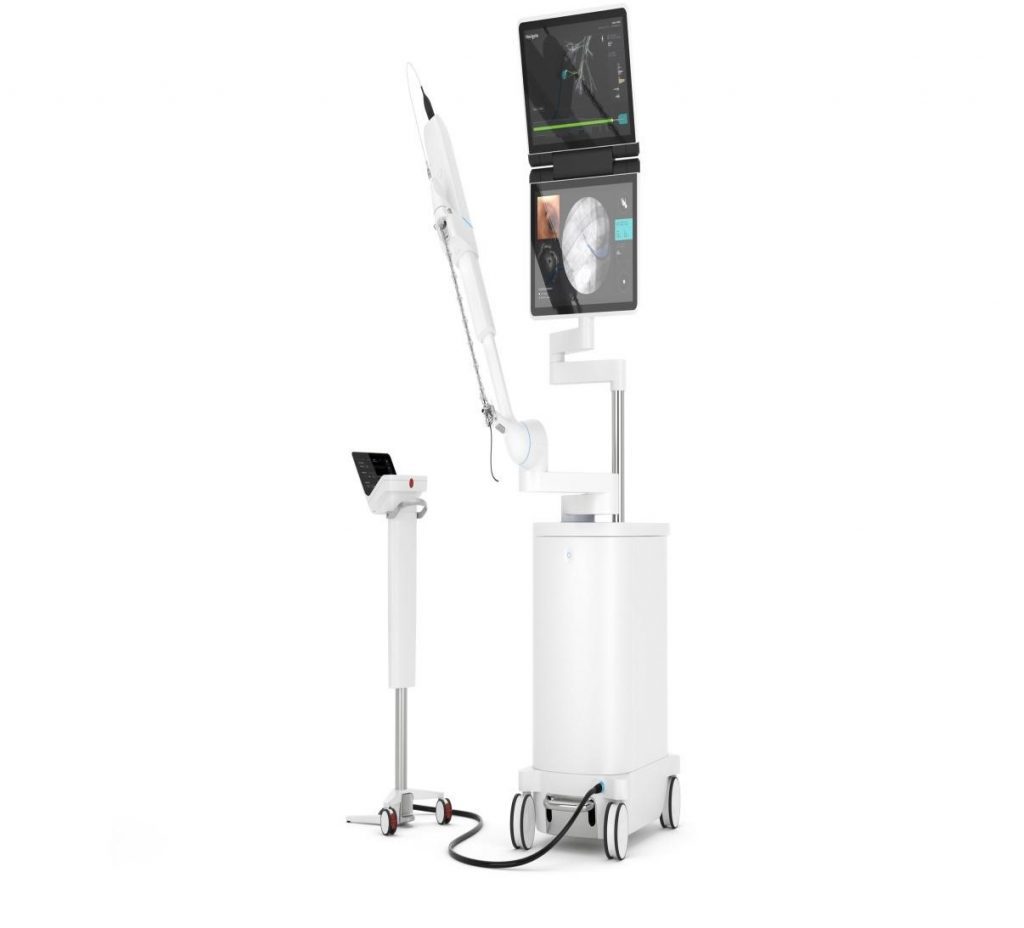

3. Mako By Stryker:
The Mako System is robotics-assisted surgical equipment that is now available for partial knee, complete hip, and total knee surgery.
The pre-operative planning method enables precise implant placing by generating a 3D model of the patient’s body shape using data from a CT scan. It results in a plan tailored to the specific patient, which the physician may evaluate before surgery.
Modifications to the ideal implant location may be required, with data acquired during the procedure and incorporated into the CT scan model. Mako Surgical Corporation, the original developer of the technique, was purchased by Stryker in 2013 for $1.65 billion.

4. NAVIO By Smith & Nephew:
The NAVIO Surgical System also employs robotic-assisted technologies in complete knee replacement surgeries. Instead of utilizing preoperative CT scans, bone mapping is accomplished during the surgery to provide a 3D depiction of the bone structure.
Before making any incisions, the surgeon utilizes this computer model to precise position the implant and maintain tissue balance.
The surgeon then utilizes a robotics-assisted hand tool to help in the surgical operation based on the results of the bone mapping. In April 2018, the FDA granted 510(k) approval to the NAVIO Surgical System.
Smith & Nephew has teamed up with Osso VR, a surgical training business, to develop a module for the NAVIO Surgical System.
This module, which includes clinically supported virtual reality (VR) simulations of the surgery, is intended for use by practicing surgeons and residents studying the robotics-assisted technique.
Dr. Cyril (Jay) Kruse, Medical Director of Orthopedic Surgery at Unity and Mercy Hospitals, studied both the Mako and NAVIO systems and recommends NAVIO for its accuracy as well as the elimination of the necessity for CT scans.
He points out that the CT scan is not only a time-consuming and expensive operation, but it also exposes people to hazardous radiation.

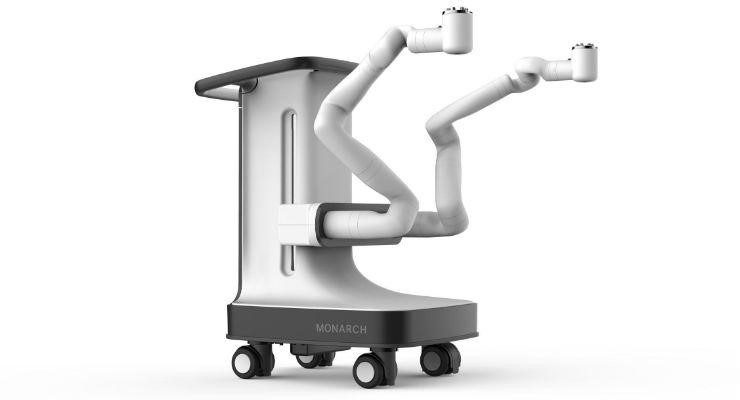
5. Monarch By Auris Health:
In March 2018, the FDA granted 510(k) approval to Auris Health’s bronchoscopic gadget, the Monarch System.
The robotics-assisted method includes a video game-like joystick into the treatment, which the surgeon uses to move a flexible robotic endoscope through the lungs’ branches.
A revolutionary new technique for employing lung endoscopic treatments, this system combines a continuous bronchoscope image with computer-guided navigation and precise instrument control.
It combines classic endoscopic perspectives with computer-guided navigation based on patient-specific 3D models.
Johnson & Johnson’s Ethicon division paid $3.4 billion for Auris Health in 2013. The transaction also includes $2.35 billion in contingent payments, bringing the total to a mind-boggling $5.75 billion.
Advantages Of Robotic Surgery For The Welfare:
Surgeons may also employ robotic-assisted surgery to deliver less intrusive and more precise solutions for a wide range of complex surgical procedures, from knee replacements to cancer therapy.
Surgical instruments and a high-definition 3-D display are put into the body via small incisions. The surgeon then manipulates several pieces of equipment from a nearby console to carry out the procedure.
During robotic-assisted surgery, the surgeon utilizes master orders to manage the tools, and the devices turn the surgeon’s motions into particular movements inside the body. The surgical equipment reacts to the instructions he or she provides.
1. Minimally Invasive:
Doctors don’t have to touch the body, hence the number of surgical incisions is lower than in conventional procedures. As a result, the surgeon’s hands are protected from bleeding and infection by the robotic arms, which limits the risk of accidental punctures and nicks.
Robotic surgery is an excellent option for anybody seeking an operation in difficult-to-reach areas of the body.
When major blood vessels or other vital organs are close, the treatment is riskier. In some cases, a larger incision may be necessary to allow the surgeon to see well enough to carry out the treatment.
2. High Surgical Accuracy:
Few surgeries, from orthopedic operations to neurological treatments, need a high level of precision. A single slip or misplaced collection of forceps in the scalpel can inflict damage or even death to the patient.
Robotic surgery robots are not sensitive to shaking or other strain-related movements that a human surgeon may experience. If the controller’s hands tremble, the machine’s software adjusts for the motion, yet the operation does not hamper.
Each robotic hand can rotate 360 degrees several times, which human hands cannot accomplish. It allows them to move more freely. It has microscopic joints that, like a human wrist, enable each arm to flex.
It is an enhancement over traditional laparoscopic tools, which are straight and unable to bend, making them more complex to use. It equips with a 3D high-definition camera, which allows for a sharper view of the surgical site even during open surgery.
3. Less Trauma:
Surgeries that traditionally need a week-long post-operative hospital stay may someday convert to outpatient procedures. For example, a liver resection following a standard protocol will keep a patient in the hospital for a week or longer.
Having a robot decreases your stay in the hospital to one or two days, which minimizes trauma in the patients.
4. Reduced Surgeon Fatigue:
Surgeries, particularly ones lasting many hours, are stressful for the attending surgeon. The physicians are on their feet for hours at a time, completing the operation and caring for the patient.
Robotic surgery allows the surgeon to carry out their duties while sitting back and relaxing. It might help keep surgeons alert and focused throughout their surgeries, avoiding errors caused by weariness, and lowering the danger of medical malpractice.
5. Less Chance Of Infection:
If you have an infection after any medical operation, it might delay your recovery and keep you in the hospital for a longer period. Somebody areas are more susceptible to infection than others, particularly when vast body areas expose due to extensive incisions.
However, since robotic surgery is less intrusive, the chance of infection is reduced, and so the hazards associated with infection are removed.
6. Less Pain:
With fewer incisions and more precision, you will have less discomfort both before and after surgery. You’ll also be less dependent on opioids throughout rehabilitation, which lowers your chance of addiction.
7. Less Blood Loss:
Blood loss is minimal during robotic surgery, and blood transfusions are seldom required. Blood loss may lead to difficulties in specific surgery, resulting in substantially longer recovery times.
8. Faster Recovery:
Because robotic surgery is less intrusive, the body will recuperate faster than with traditional surgery. Everyone is unique, and the time it takes to recuperate is determined by the individual’s circumstances.
However, most people can resume routine responsibilities, including employment, within a few weeks following robotic-assisted surgery.
You may save money on the often high expenditures of an inpatient hospital stay and return to your regular life more soon with a potentially shorter healing time. Because there is less physical discomfort, you will most likely have less scarring after you recuperate.
Medical Malpractice Claims & Robotic Surgery:
AUI cautions us that there is a danger of mechanical failure in robot-assisted surgery, in addition to the risk of human mistakes while operating the robotic system.
System components such as robotic arms, cameras, robotic towers, binocular lenses, and types of equipment might fail.
In other circumstances, the electrical current in the robotic device might escape and be applied to nearby tissues, resulting in burn damage. These palsies may be due to improper posture or direct nerve compression during robot-aided surgeries.
In addition, robotic surgery takes longer than conventional surgery in surgical facilities with lower robotic volume or by less experienced surgeons.
Some of the known robotic surgical mishaps are as follows:
- Tool fragments that have been broken or burned that have fallen into the patient
- Electrical sparks emitted by robotic equipment
- Unintentional motions
Human mistakes, robotic malfunction, or surgical technique-related risks might all be blamed for a patient’s problems if they arise during robotic surgery. In many situations, the maker of the robotic equipment is held liable.
Staff in the operating room and doctors in charge of the procedure have also been sued due to faulty equipment training and failing to advise users of the hazards involved.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
- Is Laparoscopic Surgery Better Than Robotic Surgery?
Robotic surgery is a superior choice since it was created to address the drawbacks of laparoscopic surgery, such as 2-D imaging, a poor ergonomic posture of the surgeon, and a restricted range of motion of the surgical tools.
Robotic surgery has the potential to increase surgeons’ ability to see and do their tasks.
- Is Robotic Surgery Harmless?
Both patients and physicians are seen to be safe while undergoing robotic surgery. It is also incredibly beneficial:
- Gynecologic and head and neck operations may be performed with this device.
- Patients may find it challenging to recover from open operations.
- Those who do not want to suffer from pain, blood loss, or discomfort
- Is Robotic Surgery Covered By Insurance?
An insurer that supports minimally invasive operations covers robotic surgery. However, your health plan’s features and advantages will play a role.
Future of Robotics In Surgery:
Many surgeons have discussed using technology in surgery, as the healthcare industry has previously used technologies such as robots and Artificial Intelligence (AI). AI and robots are being used to analyze patients and get accurate health data at a quicker rate.
It saves a lot of time in the results review process, and the earlier the findings of any test are available, the sooner the therapy may begin.
We now have robotic surgeons that assist physicians during surgery. Robotic surgeons provide more accurate outcomes in the manner they do any procedure. By using a robotic surgical system, surgeons can get a sharper picture of what is happening within the body.
Robots can reach a better part of the body with a little incision in the body, but doctors often need a much bigger area to be sliced to look deeper, which is not the case with robotic surgeons.
Future surgical procedures might be carried out entirely by robots. In the future, robots will almost certainly take the role of doctors. Surgical precision would improve, increasing the likelihood of a positive outcome.
The creation of surgical robots will take time to deploy, but we will witness this revolution in the healthcare industry sooner or later.

Subscribe to Our Latest Newsletter
To Read Our Exclusive Content, Sign up Now. $5/Monthly, $50/Yearly
Categories: Technology
Source: vtt.edu.vn